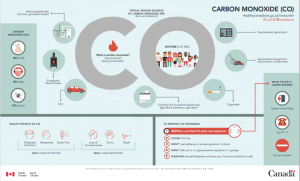
Between 2000 and 2013, 1,125 people died from carbon monoxide poisoning in Canada.”
Statistics Canada
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a leading cause of unintentional poisoning deaths in Canada and North America. CO is a colourless, odourless, toxic gas that can cause immediate harm if unnoticed, including coma and death.
CO is produced by appliances that run on fossil fuels (wood, gas, oil or coal), such as:
- Clothes dryers
- Ovens
- Water heaters
- Fireplaces (wood or gas)
- Gas or oil furnaces
- Exhaust fumes from cars

Prevention at home
Be aware of the hazard.
CO is a highly poisonous gas, often referred to as “the silent killer” because you can’t see it, touch it or smell it.
Know the symptoms of CO poisoning.
- They are similar to the flu – nausea, headache, burning eyes, confusion and drowsiness – except there is no fever. These symptoms are often either ignored or misdiagnosed.
- If they appear, immediately get everyone, including pets, outside to fresh air and call 911 or your local fire department.
Eliminate CO at the source.
Fuel-burning appliances are a common source of CO when they malfunction; as well, the gas can build up due to poor venting or confined spaces, such as you find in a furnace room, garage, cabin, tent, RV, boat cabin or camper. Have a TSSA-certified fuel technician inspect your fuel-burning appliances every year.
Install CSA-approved CO alarms in your home to alert your family to the presence of the gas.

The nature of carbon monoxide poisoning requires proactive safety measures – waiting until after the poisoning has occurred is too late. Without a carbon monoxide alarm, you can’t detect this poisonous gas.
CO alarms
As of 2022, CO alarms are mandatory in all provinces and Yukon Territory, either through provincial law or adoption of the National Building Code of Canada.
Alarms with digital displays let you see if there’s a change in your home’s air quality before it reaches dangerous levels. There are also combination smoke and CO alarms; some models even “talk” by calling out the danger when it sounds.
Installation
- Follow the manufacturer’s instruction or ask your local fire department for installation locations.
- Place the alarm where you can easily see the digital readout. Unlike smoke that rises, CO mixes with air so CO alarms can be installed at any height in a room.
- Install CO alarms on every floor of your home and outside sleeping areas.
- Do NOT install CO alarms in garages.
Maintenance
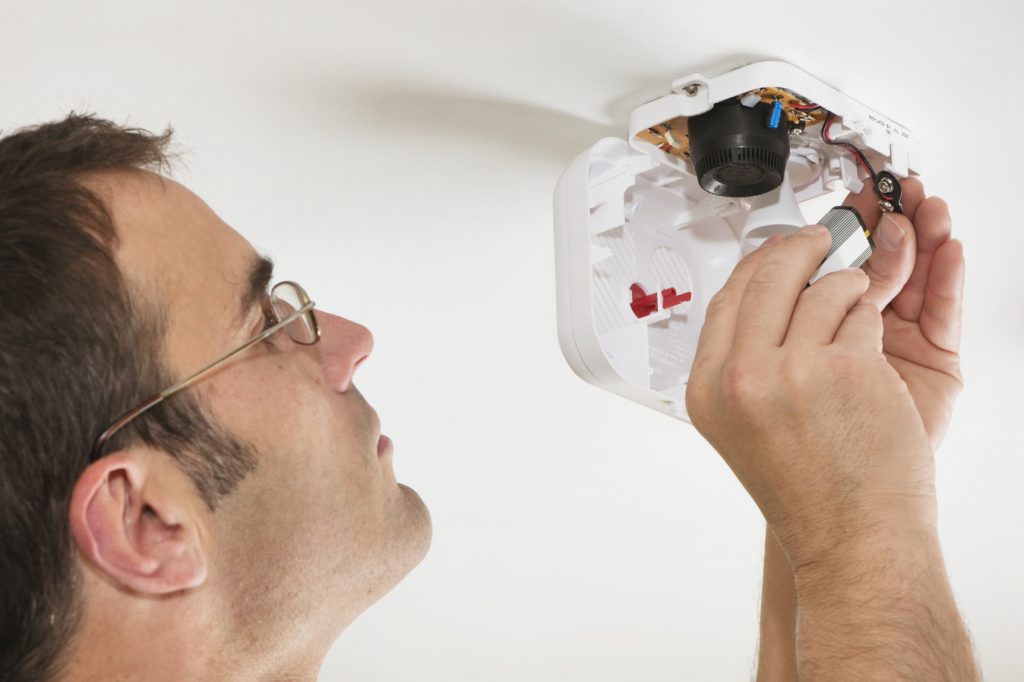

- Test the alarms monthly using the test button.
- Remove dust and other airborne debris by lightly vacuuming alarms.
- Replace batteries at least once a year.
- Replace the unit according to the manufacturer’s instructions, as recommended by the National Fire Protection Association. Alarms wear out! Sensors weaken and become obstructed over time.